- 热度指数:2479 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空间限制:C/C++ 64M,其他语言128M
- 算法知识视频讲解
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
A Complete Binary Tree (CBT) is a tree that is completely filled, with the possible exception of the bottom level, which is filled from left to right.
Now given a sequence of distinct non-negative integer keys, a unique BST can be constructed if it is required that the tree must also be a CBT. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of this BST.
输入描述:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=1000). Then N distinct non-negative integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space and are no greater than 2000.
输出描述:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of the corresponding complete binary search tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
输入
10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0
输出
6 3 8 1 5 7 9 0 2 4
//利用完全二叉树的性质就可以很简单地解决这道题
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000 + 10;
int tree[maxn], num[maxn];
int n, idx = 1;
void InOrder(int root) {
if (root > n) return;
InOrder(root * 2);
tree[root] = num[idx++];
InOrder(root * 2 + 1);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &num[i]);
sort(num + 1, num + n + 1);
InOrder(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
printf("%d", tree[i]);
if (i < n) printf(" ");
}
return 0;
} //complete binary search tree
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int key=-1;
node* left=NULL;
node* right=NULL;
};
vector<int> list;
node* record[2020];
vector<int> record2;
int n;
void level_traversal(node* root){
queue<node*> que;
que.push(root);
node* point;
while(!que.empty()){
point=que.front();
if(point->left!=NULL)que.push(point->left);
if(point->right!=NULL)que.push(point->right);
cout<<point->key;
que.pop();if(!que.empty())cout<<" ";
}
}
void middle(node* root){
if(root==NULL)return;
middle(root->left);
record2.push_back(root->key);
middle(root->right);
}
void build_bst(){
int cnt=1;
int tem;
queue<int> que;
que.push(cnt);
while(cnt<=n){
tem=que.front();
record[tem]->key=tem;
if(tem*2<=n){
record[tem]->left=record[tem*2];
que.push(tem*2);
}
if(tem*2+1<=n){
record[tem]->right=record[tem*2+1];
que.push(tem*2+1);
}
que.pop();cnt++;
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<2020;i++)record[i]=new node;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>temp;
list.push_back(temp);
}
sort(list.begin(),list.end());
build_bst();
middle(record[1]);
for(int i=0;i<record2.size();i++){
record[record2[i]]->key=list[i];
}
level_traversal(record[1]);
return 0;
} package com.jingmin.advanced2;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author : wangjm
* @date : 2020/6/9 21:21
* @discription : https://www.nowcoder.com/pat/5/problem/4115
* 建立二叉搜索树,且要求为完全二叉树(唯一),然后层次遍历输出
* <p>
* 按层次建树,中序遍历写值,再层次遍历取值
*/
public class Advanced1022 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
scanner.close();
Arrays.sort(a);
Node1022 root = setupCompleteBinaryTree(n);
ArrayList<Node1022> inOrdrList = inOrderTraversal(root);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
inOrdrList.get(i).value = a[i];
}
ArrayList<Node1022> levelOrderList = bfs(root);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Node1022 node : levelOrderList) {
sb.append(node.value).append(" ");
}
sb.setLength(sb.length() - 1);
System.out.println(sb);
}
/**
* 层次建树,初始化一个n个节点的完全二叉树(n>=1)
* 注意,这个二叉树只建立起结构,没有存入值
*/
private static Node1022 setupCompleteBinaryTree(int n) {
int count = 0;
Node1022 root = new Node1022();
Queue<Node1022> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
count++;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && count < n) {
Node1022 node = queue.poll();
if (count < n) {
node.lChild = new Node1022();
queue.add(node.lChild);
count++;
}
if (count < n) {
node.rChild = new Node1022();
queue.add(node.rChild);
count++;
}
}
return root;
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
private static ArrayList<Node1022> inOrderTraversal(Node1022 node) {
ArrayList<Node1022> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Node1022> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.lChild;
}
node = stack.pop();
list.add(node);
node = node.rChild;
}
return list;
}
private static ArrayList<Node1022> bfs(Node1022 root) {
ArrayList<Node1022> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node1022> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node1022 node = queue.poll();
list.add(node);
if (node.lChild != null) {
queue.add(node.lChild);
}
if (node.rChild != null) {
queue.add(node.rChild);
}
}
return list;
}
}
class Node1022 {
int value;
Node1022 lChild, rChild;
}
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1010;
int A[MAXN], BST[MAXN];
int n, idx = 0;
void inorder(int root) {
if (root > n) return;
inorder(2 * root);
BST[root] = A[idx++];
inorder(2 * root + 1);
}
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d", &A[i]);
sort(A, A + n);
inorder(1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) printf("%d ", BST[i]);
printf("%d", BST[n]);
return 0;
} #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1010;
int tree[MAXN],a[MAXN];
int n,index=1;
void inOrder(int root)
{ if(root>n) return; inOrder(root*2); tree[root] = a[index++]; inOrder(root*2+1);
}
int main()
{ cin>>n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i]; sort(a+1,a+n+1); inOrder(1); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(i==n) cout<<tree[i]<<endl; else cout<<tree[i]<<" "; } return 0;
}
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <stack> using namespace std; int main() { // 读入数据 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int N; cin >> N; vector<int> nums(N), cbst(N); for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { cin >> nums[i]; } // 对nums排序并填充cbst sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); int idxNums = 0, index; bool visited; stack<pair<int, bool> > stk; stk.push(make_pair(0, false)); while(!stk.empty()) { index = stk.top().first; visited = stk.top().second; stk.pop(); if(index < N) { if(visited) { cbst[index] = nums[idxNums++]; } else { stk.push(make_pair(2*index+2, false)); stk.push(make_pair(index, true)); stk.push(make_pair(2*index+1, false)); } } } // 输出 cout << cbst[0]; for(int i=1; i<N; i++) { cout << " " << cbst[i]; } return 0; }
直接用完全二叉树的性质来,左右孩子分别为根节点2倍和2倍+1,。通过该性质对有序的排列进行中序遍历可建树。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int node[1010],tree[1010];
int N,pos;
void creatTree(int root){
if(root>N) return;
int lchild=root*2,rchild=root*2+1;
creatTree(lchild);
tree[root]=node[pos++];
creatTree(rchild);
}
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a<b;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d",&node[i]);
}
sort(node,node+N,cmp);
pos=0;
creatTree(1);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
printf("%d",tree[i]);
if(i<N){
printf(" ");
}
}
}
用数组表示完全二叉树
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int Max=1010;
int n,num[Max],CBT[Max],id;
void Inorder(int root) {
if(root>n) {
return ;
}
Inorder(root*2);
CBT[root]=num[id++];
Inorder(root*2+1);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
}
sort(num,num+n);
Inorder(1);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
printf("%d",CBT[i]);
if(i<n) printf(" ");
}
return 0;
} /*
int [] nums = newint[];
for(){
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int [] trees = new int[];
dfs(int index){
if(index > nums.length){
return;
}
dfs(index*2+1);
trees[index] = nums[j];
j++;
dfs(index*2+2);
}
dfs(0);
*/分享个伪代码把 很简单

更多PAT甲级题解--acking-you.github.io
题目
题目解析
题目大意:
二叉搜索树大家都不陌生,这个题需要你构造的二叉树二叉搜索树同时也是完全二叉树,然后打印出它的层序遍历序列。
- 这道题把我坑到了,我竟第一时间想的并不是从它的中序重新构建出这颗二叉树,我开始想的非常复杂🤣
首先根据二叉搜索树的性质可知它的中序遍历序列(直接排个序),实际上知道了中序遍历序列就已经可以构造出对应的完全二叉树了,根据中序利用递归反向推导即可。
然而我却第一时间想到的是先求出这颗完全二叉树的层数,然后根据这个求出这颗完全二叉树左子树的个数,然后便可以得出这颗完全二叉树的根结点(由于有序,且根结点的左边都是小于根结点的数,所以直接根据左子树结点个数可得出根节点的编号),我一心只想着求出这个总根之后再取构建完全二叉树,熟不知给你的本就是一棵完全二叉树,只需要根据中序直接构建即可!
看看我这错误代码🤣(实际数据量不大都能过
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int N;
int* nums;
int* res;
int left_sum;
void pre_handle() { //由于是完全二叉树,所以设层数为i则有,2^(i-1)-1<=N<=2^i-1
int i = 1;
while ((1 << i) - 1 < N)i++;
int leave = N - (1 << (i - 1)) + 1 > (1 << (i - 1)) / 2 ? (1 << (i - 1)) / 2 : N - (1 << (i - 1)) + 1; //判断是否半满,如果大于半满则左子树的尾数为半满个数
left_sum = leave + ((1 << (i - 1)) - 2) / 2; //得出左子树总个数
}
void Input() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> N;
nums = new int[N];
res = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> nums[i];
}
sort(nums, nums + N);
pre_handle();
}
void BST(int root, int l, int r) {
if (l > r)
return ;
int t_l = l, t_r = r, node;
if (root == 0) {
node = l + left_sum;
}
else node = (t_l + t_r) % 2 == 0 ? (t_l + t_r) / 2 : (t_l + t_r) / 2 + 1;
res[root] = nums[node];
BST(root * 2 + 1, l, node - 1);
BST(root * 2 + 2, node + 1, r);
}
void print() {
BST(0, 0, N - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (i != N - 1)
cout << res[i] << ' ';
else
{
cout << res[i];
}
}
}
int main() {
Input();
print();
return 0;
} 正确代码详解
实际**们只要对中序遍历理解的够深,基本就能秒了。
由于我们经过排序后的数据就是中序遍历,而中序遍历都是 左-根-右 ,所以在我们重新构建完全二叉树的时候也需要是 左-根-右 ,对于从数组下标0开始的完全二叉树,有左子树为 i*2+1 ,右子树为 i*2+2 。由于子树都是抽象的数据,根则是具体的,所以需要不断递归直到得到根就开始给完全二叉树赋值。
- 由于用数组存下完全二叉树的序列后,它的序列就是层序遍历的序列。。。所以直接打印即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int N; int* nums; int* res; int idx = 0; void Input() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin >> N; nums = new int[N]; res = new int[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { cin >> nums[i]; } sort(nums, nums + N); } void creatCBT(int root) { if (root >= N) return; creatCBT(root * 2 + 1); //左子树 res[root] = nums[idx++];//根 creatCBT(root * 2 + 2); //右子树 } void print() { creatCBT(0); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { cout << res[i] << ' '; } } int main() { Input(); print(); return 0; }
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,cnt=0;
vector<int> in,data,list;
void dfs(int index){
if(index>=n) return ;
dfs(index*2+1);
in.push_back(index);
dfs(index*2+2);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
data.resize(n),list.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d", &data[i]);
sort(data.begin(),data.end());
dfs(0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
list[in[i]]=data[i];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d%c",list[i],i==n-1?'\n':' ');
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
(720)#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1001;
int numberSequence[MAXN];
int CBST[MAXN];
int N,pos=1;
void createCBST(int root){//中序遍历创建CBST
if(root>N){
return;
}
int left=root*2,right=root*2+1;
createCBST(left);
CBST[root]=numberSequence[pos++];
createCBST(right);
}
int main(){
fill(numberSequence,numberSequence+MAXN,-1);
fill(CBST,CBST+MAXN,-1);
cin>>N;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
cin>>numberSequence[i];
}
sort(numberSequence+1,numberSequence+N+1);
createCBST(1);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
if(i!=1) printf(" ");
printf("%d",CBST[i]);
}
} a = int(input())
i,m,p,q = 1,[],256,[]
while a > i:
m.extend([p * (2 * j + 1) / i for j in range(i)])
a -= i
i *= 2
m.extend([p * (2 * j + 1) / i for j in range(a)])
n = dict(zip(sorted(m),sorted(map(int,input().split()))))
while n:
for i in list(n):
if i / p == i // p:
q.append(str(n[i]))
del n[i]
p /= 2
print(' '.join(q))
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,now,seq[1000],insert[1000];
void bst(int root) {
if (root >= n) return;
bst(root * 2 + 1);
seq[root] = insert[now++];
bst(root * 2 + 2);
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> insert[i];
sort(insert, insert + n);
bst(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << (i == 0 ? "" : " ") << seq[i];
return 0;
} 
// 递归法创建二叉树,返回根节点位置
Posnode BuildCBST(int *sorted_array, int Num) {
Posnode pos_root = (Posnode)malloc(sizeof(CBSTnode)); // 初始化根节点
int deep = floor(log(Num) / log(2)) + 1;
int index = pow(2, deep - 1) - max(0, 3 * pow(2, deep - 2) - Num - 1);
pos_root->key = *(sorted_array + index - 1);
if (index - 1>0)
pos_root->leftchild = BuildCBST(sorted_array, index - 1);
else pos_root->leftchild = NULL;
if (Num - index > 0)
pos_root->rightchild = BuildCBST(sorted_array + index, Num - index);
else pos_root->rightchild = NULL;
return pos_root;
} 
/*
Sologala @github https://github.com/Sologala/PAT_OJ
PAT_oj No.1064_Complete_Binary_Search_Tree
*/
思路
题目时要求一个完全二叉搜索树(CBT)的层次便利序列
如果这样一个CBT 是满二叉树。那么就可以层次遍历快速的。
但是如果给出的二叉树是非满二叉树如下图所示,那么我们可以对该🌲 处理一下。先把最后一层的节点拆掉,这样留下来的必然是一颗满二叉树,通过数组可以快速的找到树根,然后层次便利。
拆最底层节点
既然是BST 那么 对节点信息sort之后必然是 该树的中序序列。而 树的遍历有一个性质就是 叶子结点在遍历中的相对位置不变,且这里是完全二叉树。如下图所示,可以发现一下规律。
中序序列 从第一个开始 没跳一个都是底层的叶子。

而底层叶子结点的个数可以用下面的方法求,通过树的基本性质
//计算最后一层的数量。
int h =log(cnt)/log(2)+1;
int a =cnt-pow(2,(h-1))+1;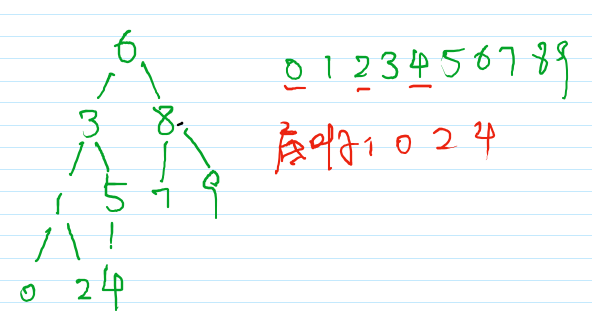
这样就把底层叶子拆掉 ,保存起来,对剩下的完全满二叉树 层次遍历,最后在加上最后一层的叶子结点。

而满二叉树的遍历在这里因为树用的数组来存储树,所以应该在队中存储 数组的开始和结束。以及子树的开始和结尾。而树根这是(low+high)/2(ps这里我的数组 是从1开始的,从0开始需要变化一下)
ac_code
/*
Sologala @github https://github.com/Sologala/PAT_OJ
PAT_oj No.1064 Complete Binary Search Tree
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
bool tag=false;
vector<int> T;
int main(){
int cnt;
scanf("%d",&cnt);
T.resize(cnt+1);
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++)
{
scanf("%d" ,&T[i]);
}
sort(T.begin()+1,T.end());
//计算最后一层的数量。
int h =log(cnt)/log(2)+1;
int a =cnt-pow(2,(h-1))+1;
vector<int> last_level;
for(int i =1;a>0;i++){
last_level.push_back(T[i]);
T.erase(T.begin()+i);
a--;
}
//此时的T 是一个满二叉树 从中间位置开始读取就ok了。
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(1);
Q.push(T.size()-1);
while(!Q.empty()&&!T.empty()){
//dequeue
int low =Q.front();
Q.pop();
int high=Q.front();
Q.pop();
if(low>high) break;
int r =(low+high)/2;
//ourput
if(!tag) {printf("%d",T[r]);tag=true;}
else printf(" %d",T[r]);
//push left_side
Q.push(low);
Q.push(r-1);
//push right_side
Q.push(r+1);
Q.push(high);
}
//output the last_level
for(vector<int>::iterator it=last_level.begin();it!=last_level .end();it++){
//ourput
if(!tag) {printf("%d",*it);tag=true;}
else printf(" %d",*it);
}
return 0;
} #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
int n,data[maxn],cbst[maxn],index=0; //data存储输入的序列,cbst存储完全二叉查找树
void create(int root){ //按照中序来构建cbst,此csbt按顺序即为层序序列
if(root>n-1) return; //超过给定结点数,即为空结点,直接返回
create(2*root+1); //(根为0)完全二叉树结点i的左子女为2i+1,右子女为2i+2
cbst[root]=data[index++];
create(2*root+2);
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>data[i];
sort(data,data+n); //将输入序列升序排列,即为BST中序遍历序列
create(0);
cout<<cbst[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
cout<<" "<<cbst[i];
return 0;
} #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int CBT[1001];
int nums[1001],ind = 1;
int n;
void build(int i) {
if (i > n)return;
build(2 * i);
CBT[i] = nums[ind]; ind++;
build(2 * i + 1);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &nums[i]);
sort(nums + 1, nums + n + 1);
build(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i != 1)cout << " ";
cout << CBT[i];
}
return 0;
} //这个树既是二叉排序树也是完全二叉树。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e3+5;
int n,cnt,A[maxn],node[maxn];
void build(int rt){
if(rt>n) return ;
build(2*rt);
node[rt]=A[++cnt];
build(2*rt+1);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&A[i]);
sort(A+1,A+1+n);
build(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(i==1) printf("%d",node[i]);
else printf(" %d",node[i]);
return 0;
}


































