魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.
<center>
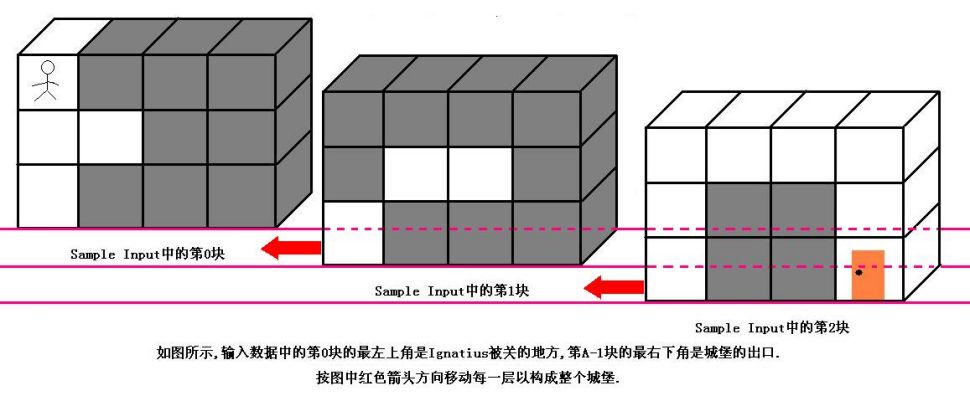 </center>
</center>






















#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <cstdio> #include <sstream> #include <deque> #include <functional> #include <iterator> #include <list> #include <map> #include <memory> #include <stack> #include <set> #include <numeric> #include <utility> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int A, B, C, T; struct point { int x, y, z; int t; point(int x=0, int y=0, int z=0, int t=0): x(x), y(y), z(z), t(t) {} }; int direct[][3] = {{1,0,0}, {-1,0,0}, {0,0,1}, {0,0,-1}, {0,1,0}, {0,-1,0}}; int Map[55][55][55]; int BFS() { queue<point> que; que.push(point(0,0,0,0)); while(que.size()) { point p = que.front(); que.pop(); if(p.t > T) continue; if(p.x == A-1 && p.y == B-1 && p.z == C-1) return p.t; for(int k=0; k<6; ++k) { int nx = p.x + direct[k][0]; int ny = p.y + direct[k][1]; int nz = p.z + direct[k][2]; if(nx >=0 && nx<A && ny>=0 && ny<B && nz>=0 && nz<C && Map[nx][ny][nz] == 0) { que.push(point(nx, ny, nz, p.t+1)); Map[nx][ny][nz] = 1; } } } return - 1; } int main() { int K; scanf("%d", &K); while(K--) { scanf("%d%d%d%d", &A, &B, &C, &T); for(int a=0; a<A; ++a) for(int b=0; b<B; ++b) for(int c=0; c<C; ++c) scanf("%d", &Map[a][b][c]); printf("%d\n", BFS()); } return 0; }