全景分割网络UPSNet-网络结构分析
文章目录
论文: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.03784.pdf
代码: https://github.com/uber-research/UPSNet
UPSNet网络结构
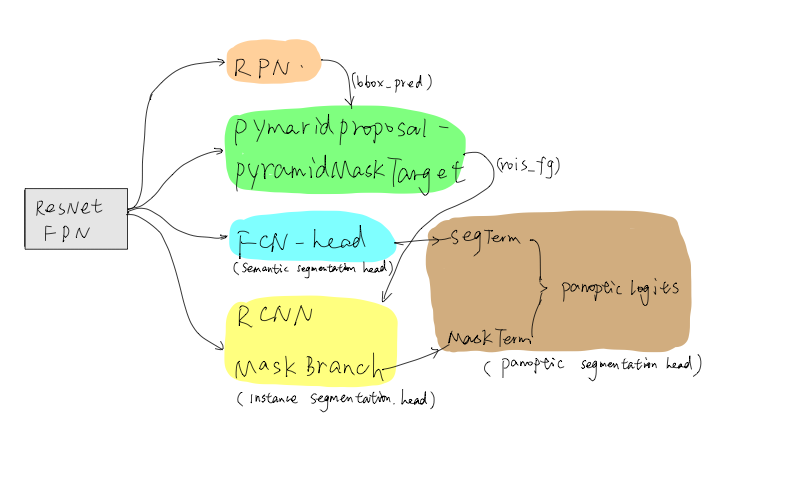
UPSNet总体结构如下图所示,包含RPN、PymaridMaskTarget生成、Semantic Segmentatin Head、Instance Segmentation Head和Panoptic Segmentation Head。
- Backbone Network:特征提取采用ResNet-FPN
- RPN:判断Proposals是否为前景,并生成bbox的坐标变换系数
- PymaridMaskTarget生成:本部分不含计算参数,用于生成前景rois
- Semantic Segmentation Head:包含FCN-Head,语义分割分支
- Instance Segmenation Head:包含RCNN,Mask Branch,预测实例的mask
- Panoptic Segmentation Head:包含SegTerm和MaskTerm,处理整合语义预测和实例的预测
以下逐一介绍各个部件
1. ResNet-FPN
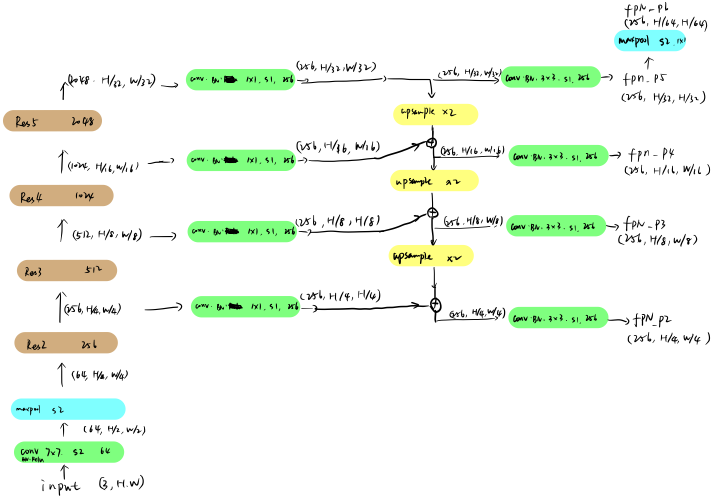
特征的提取采用ResNet后接FPN,FPN的使用充分利用了不同level特征。简图和详细的结构图如下。ResNet每个block的输出(记为 P2、 P3、 P4、 P5),分别进入一个[conv(1*1, 256)、BN],统一了Channel的个数。
- 除 P5外, Pi与其上一级 Pi+1的两倍上采样结果相加,即 Pi=Pi+UpSample(Pi+1,2);
- Pi进入[conv(3*3, 256), BN], 得到 FPN_Pi;
- P6则是 P5通过一个步长为2,size为1*1的最大池化得到。
整个模块的输出为:
| 分支名称 | channel数 | H | W |
|---|---|---|---|
| FPN_P2 | 256 | 1/4 | 1/4 |
| FPN_P3 | 256 | 1/8 | 1/8 |
| FPN_P4 | 256 | 1/16 | 1/16 |
| FPN_P5 | 256 | 1/32 | 1/32 |
| FPN_P6 | 256 | 1/64 | 1/64 |
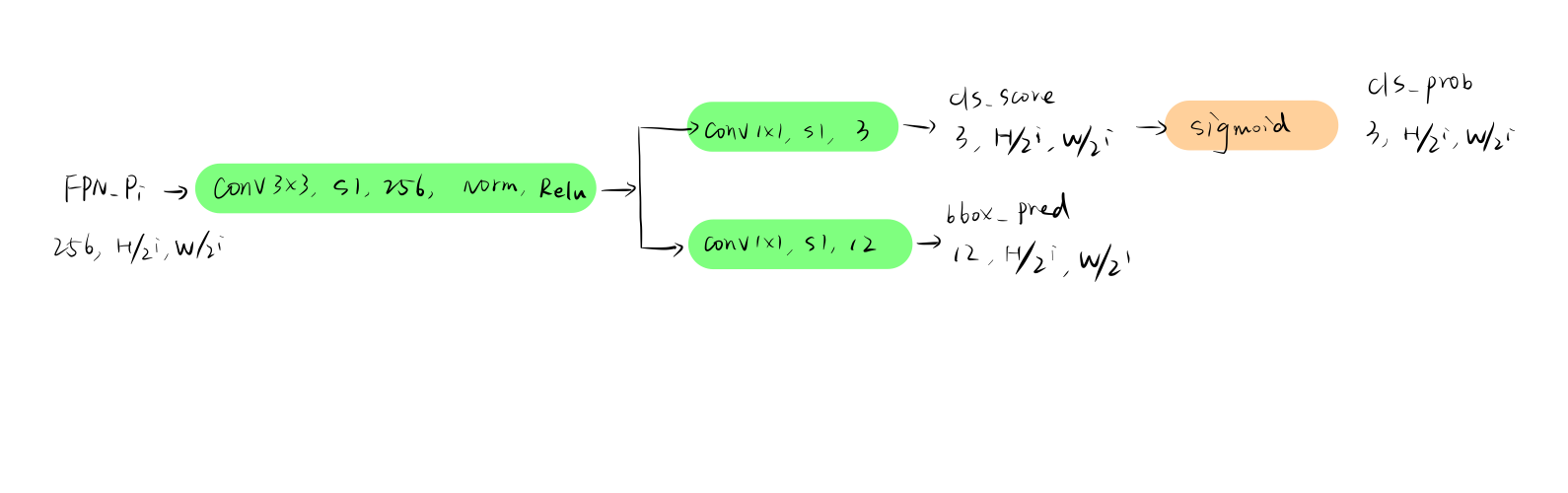
2. RPN
RPN是用来生成判断proposal是否为roi的子网络,FPN的每一个分支 FRN_Pi都经过RPN,得到了特征图单个像素点对应anchor的三个信息:
- 该anchor是前景的分数
- 该anchor是前景的概率
- 该anchor和实际gt bounding-box四个坐标的变化参数
由于每个像素点生成的anchor数为3,因此channel为3, box的Channel则为4*3=12.
网络结构如下图所示:
3. PyramidMaskTarget生成
3.1 PyramidProrosal
该层不含训练参数,单纯从不同大小的features maps中用于生成proposals,并筛选得到最有可能包含roi的2000(随设置参数而定)个proposal。具体计算流程如下:
- 对FPN的多个输出分支,执行相同的操作
- 在特征图每个像素点上,生成3个anchors,共计生成 3∗H/i2∗W/i2个anchors
- 根据RPN得到anchor是前景的得分,对生成的anchor进行排序,并取前N1个
- 根据RPN得到anchor的box坐标调整系数,调整anchor的box坐标
- 执行NMS算法,然后取score前N2个,得到该分支的proposals
- 收集所有分支的proposals,取score前N3的proposals,得到ROIS
该层的输出为ndarray, shape=(2000, 5),第二维的第一位是batch_inx,由于batchsize为1,因此第一位都为0.
3.2 PyramidMaskTarget
该层同样不包含训练参数,两个主要函数add_proposals,sample_rios.
add_proposals:
该函数实现了将2000个anchor信息添加到单张图片的roidb标注中。
初始roidb为:
{
'boxes':ndarray, shape=(8, 4),
'segms':list, len=8,
‘seg_areas’, list, len=8
'gt_classes':ndarray, len=8, [1 1 1 3 3 3 3 6]
'gt_overlaps':稀疏矩阵, bbox和gt_box的重叠比例,由于当前bbox都是gt_box,只有和其对应类别的处的值为1,shape=(num_box,num_class)
‘is_crowd’: ndarray. len=8
'box_to_gt_ind_map': ndarray, shape=(8,) bbox所对应的gt_box编号
}
通过计算RPN产生的2000个proposals和gt box的重叠比例,修改一字段的值。
- boxes,直接将2000个proposals添加到list中
- seg_areas,添加2000个0值
- gt_classes, 添加2000个0值
- gt_overlaps, 添加2000个值,若无重叠则为0,若与一个或多个重叠,取最大值
- box_to_gt_ind_map: 添加2000个值,无重叠则为-1, 重叠则为最接近的gt box在gt classes中的序号
sample_rois:
- 计算bbox和gt box的最大重叠比例,根据阈值进行划分,大于阈值记为前景,小于阈值记为背景。
- 对前后景rois进行采样,使得总和为rois-per-image, 网络中设置为512个.
- 计算512个bbox相对于其gt-box的坐标变换系数,即bbox-targets
- 更改bbox-targets的表示形式,从[class, dx, dy, dh, dw]变成[0,0,0,0,…,dx,dy,dw,dh,…,0,0,0,0],len=num-class * 4, 每四个数对应一个类别,类似于one-hot编码,只在其对应类别处有非零值
- 为每一个fg-roi制作28*28的mask
{
'labels_int32':ndarray, (512,), 若是gt-box,则为对应类别;若非gt-box,则为0,
'rois': (512, 5), 第二维第一位为batch-inx,都为0,
'bbox-targets':shape(512, 36),
'bbox-inside-weights': (512, 36),对应bbox-targets,在对应类别处值为1,1,1,1
'bbox-outside-weights': (512, 36), 对应bbox-inside-weights, 在非零值处值为1
'nongt_inds': 不是gtbox的编号, (504,) ->有8个gtbox
'mask_rois': 前景rois, shape(前景rois个数,batchinx+四个系数)=(9,5),
'rois_has_mask_int32': 有mask的rois,即属于前景的rois,shape=(512, ),是则为1,不是为0
'mask_int32': 根据fg-roi宽高比例进行调整的28*28的mask,采用和bbox-targets类似的表示方式,其shape=(前景个数, 类别数×28*28),在对应属于的类别上,连续的28*28有值(0或1),在不属于的类别上,为-1
}
4. Sementic Segmentation Head
4.1 FCN-Head
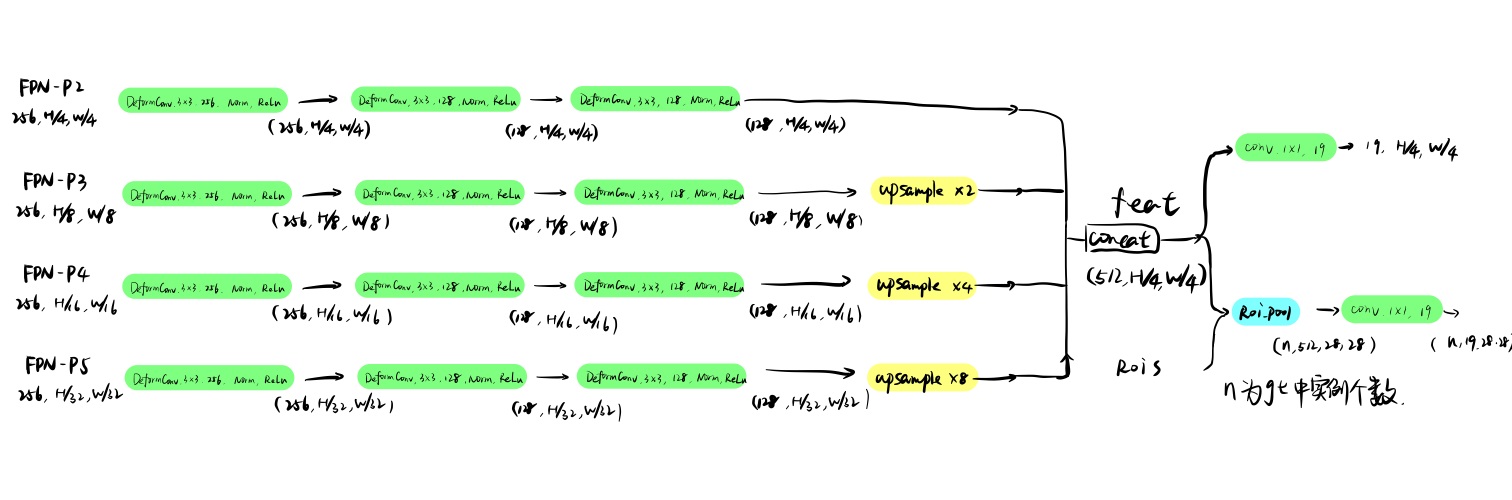
FCN-Head即用于生成语义分割的分支。承接FPN的四个分支,每个分支分别经过可变卷积,而后同一scale到H/4、W/4,concat之后再卷积得到每个像素点的在19个类别上的概率。同时计算gt-roi mask内每个像素点的在19个类别上的概率。源码及结构如下:
def forward(self, fpn_p2, fpn_p3, fpn_p4, fpn_p5, roi=None):
fpn_p2 = self.fcn_subnet(fpn_p2)
fpn_p3 = self.fcn_subnet(fpn_p3)
fpn_p4 = self.fcn_subnet(fpn_p4)
fpn_p5 = self.fcn_subnet(fpn_p5)
fpn_p3 = F.interpolate(fpn_p3, None, 2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
fpn_p4 = F.interpolate(fpn_p4, None, 4, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
fpn_p5 = F.interpolate(fpn_p5, None, 8, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
feat = torch.cat([fpn_p2, fpn_p3, fpn_p4, fpn_p5], dim=1)
score = self.score(feat)
ret = {'fcn_score': score, 'fcn_feat': feat}
if self.upsample_rate != 1:
output = F.interpolate(score, None, self.upsample_rate, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
ret.update({'fcn_output': output})
if roi is not None:
roi_feat = self.roipool(feat, roi)
roi_score = self.score(roi_feat)
ret.update({'fcn_roi_score': roi_score})
return ret
5.Instance Segmentation Head
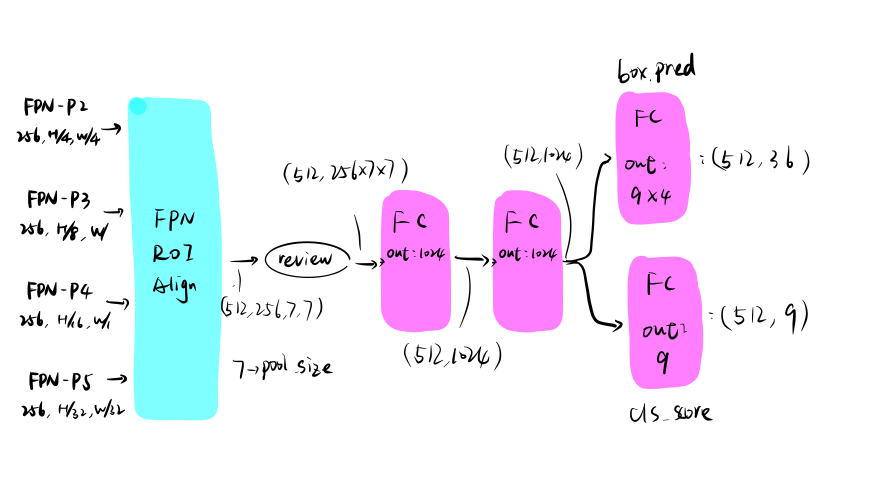
5.1. RCNN
RCNN分支用于预测512个rois(前后景)的类别和边框
- FPN的四个分支结合RPN生成的rois,使用多层次的RIAlign得到了 (512,256,7,7)的tensor,其中7为pool size.
- 将上一步得到的tensor reshape成 (512,256∗7∗7),再经过两个全连接层;
- 上一步得到的向量进入类别和box预测两个分支。
如下图所示。
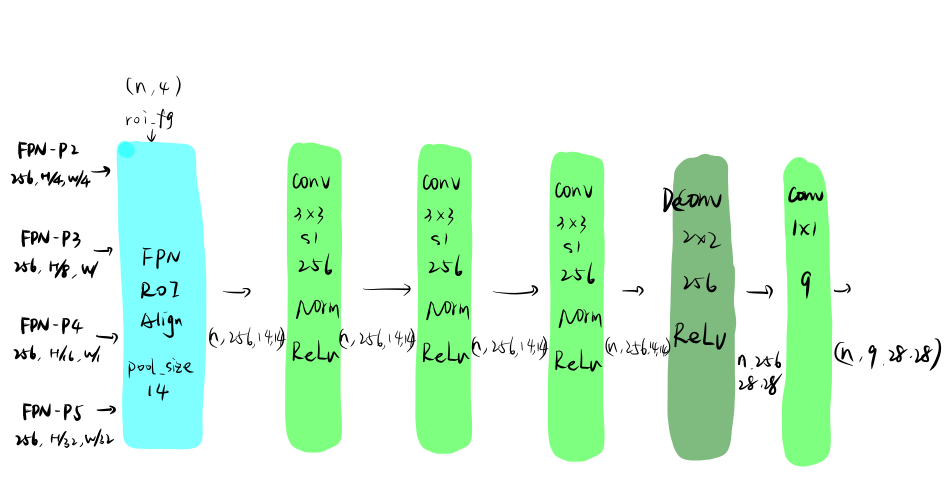
5.2 MaskBranch
MaskBranch用于生成前景roi的mask,结构如下图所示
6 Panoptic Segmentation Head
6.1 SegTerm
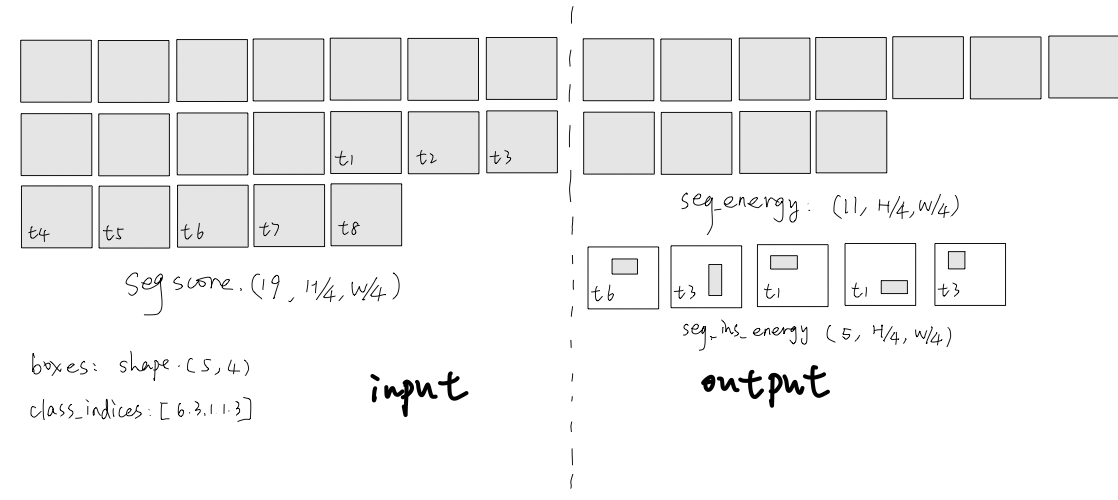
本模块的作用是把语义分割分支中不同类别的logit取出来。
输入包含四项:
- seg_score是语义分割的输出结果之一,shape=(1,19,H/4,W/4);
- boxes:前景rois的bbox,假设有5个box,则shape=(5,4)
- cls_indices是每一个box的类别,eg:[6,3,1,1,3]
- class_map,语义种类共有19个,thing种类有8个,class_map即thing和语义种类的映射关系,eg: {1: 11, 2: 12, 3: 13, 4: 14, 5: 15, 6: 16, 7: 17, 8: 18}
输出包含两项: - seg_energy 直接从seg_score中取出非thing类别,shape=(11, H/4, W/4);
- seg_ins_energy 根据box的类别,从对应的seg_score中取出box内部的数值,box外为0,shape=(5, H/4, W/4)
如下图所示, ti表示第i个thing类
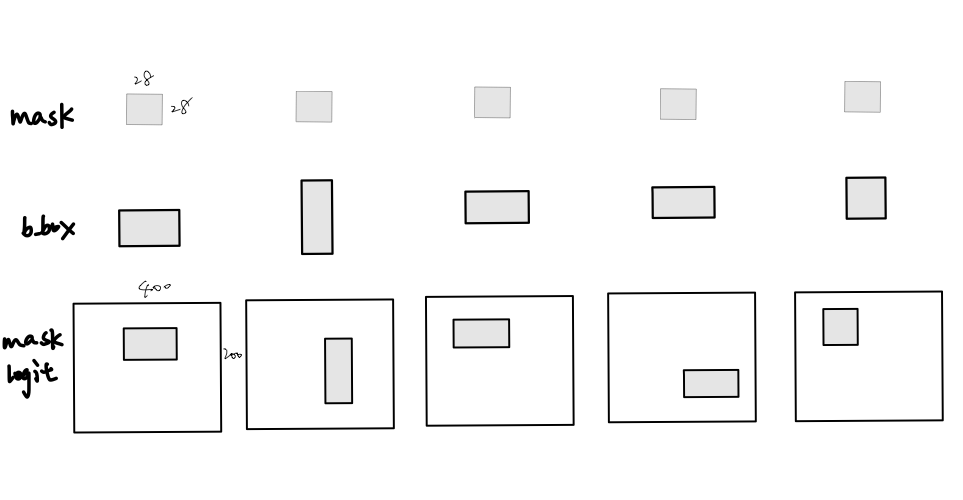
6.2 MaskTerm
本模块的作用是取出mask分支中每个检测到实例的logit
- mask大小为28*28,将其reshape成对应b-box的大小,将box内的值放到初始化为0的mask logit对应box位置处
如下图所示.
6.3 计算 panoptic logits
panoptic logits 由三项组成,语义分割部分seg-logits、实例分割部分inst_logits、和未知类预测部分void-logits。其中未知类是由gt-box中随机选出30%作为未知的类别,在本文所用的例子中,原本gt-box共有8个,现在有三个b-box被归为未知类.
void-logits
void-logits根据语义分割实例类部分logits(8,H/4,W/4)最大值减去5个b-box的logits(5,H/4,W/4)的最大值,得到(1, H/4, W/4).void-logits的计算代码如下:
void_logits = torch.max(fcn_output['fcn_score'][:, (config.dataset.num_seg_classes - config.dataset.num_classes + 1):, ...], dim=1, keepdim=True)[0] - torch.max(seg_inst_logits, dim=1, keepdim=True)[0]
inst-logits
inst-logtis则是将MaskTerm和SegTerm得到的mask-logits和seg-ins-logits直接相加。综合了两部分的预测,相当于做了一个模型融合。
inst_logits = seg_inst_logits + mask_logits
seg-logits
seg-logits则是语义分割部分stuffs部分的logtis
panoptic-logits
panoptic-logots直接将三个部分concat在一起。shape=(17, H/4, W/4), 17=11+5+1
panoptic_logits = torch.cat([seg_logits, inst_logits, void_logits], dim=1)


